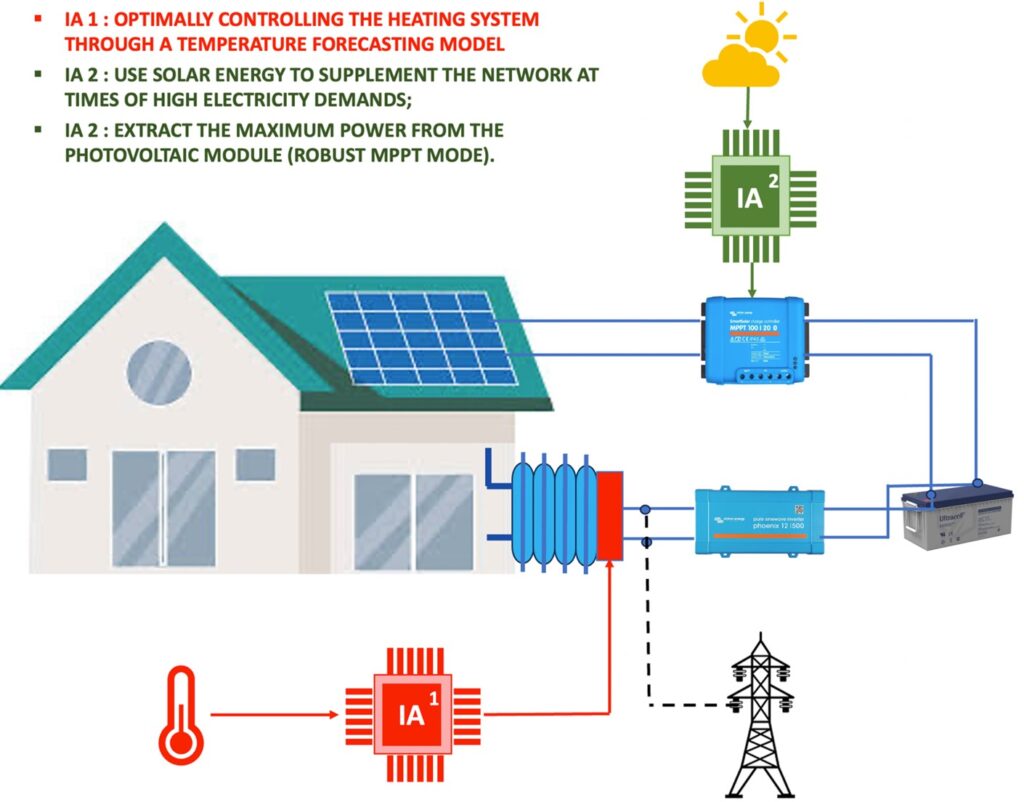
Intelligent control of a heating system to optimise energy consumption
The energy, economic, and environmental crisis affecting our society demands an improvement in energy efficiency across all sectors and a constant pursuit of frugality. Currently, the building sector accounts for 40% of final energy consumption and generates approximately 25% of greenhouse gas emissions. However, it holds significant potential for reducing energy consumption. Therefore, it is imperative to implement strategies aimed at optimizing energy consumption and increasing the use of renewable energies in building operations. Heating control plays a crucial role in this endeavor. The MIS and the LGCgE collaborate complementarily to develop predictive control techniques for heating-related consumption. The LGCgE has developed a predictive optimization strategy based on a model simulating indoor building temperatures. On the other hand, the MIS has developed predictive algorithms based on artificial intelligence to forecast meteorological parameters, electricity production by photovoltaic installations, and household consumption. Using this data as input for the predictive heating control model will improve the accuracy of indoor temperature simulations and incorporate an objective of maximizing electricity self-consumption. The control techniques developed by the MIS, based on multi-models and utilizing measurements and/or estimates of environmental parameters, will enable real-time calculation of heating power associated with minimal energy consumption.